We use cookies to make your experience better. To comply with the new e-Privacy directive, we need to ask for your consent to set the cookies. Learn more.
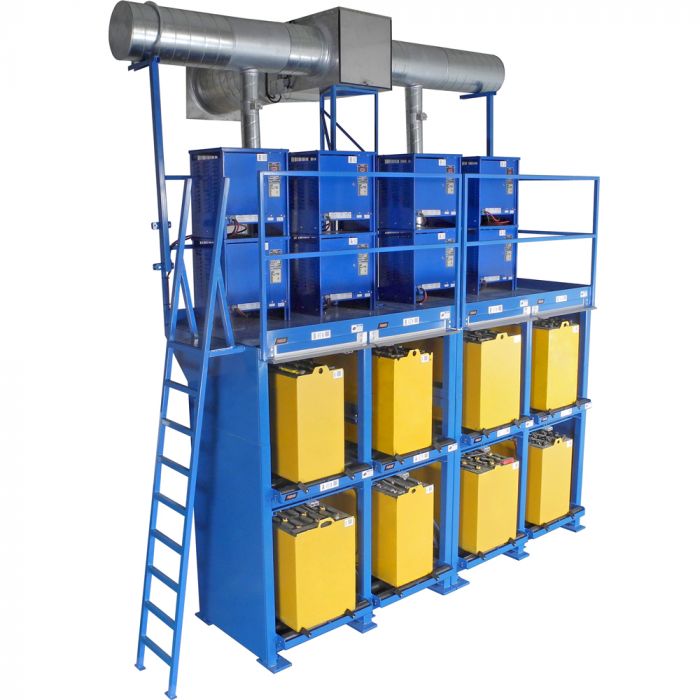
Battery Room Ventilation System
Lead-acid batteries release hydrogen gas during the charging process. Proper ventilation in the battery room is necessary to ensure potentially dangerous gases are diffused. The BHS Battery Room Ventilation System (BRVS) is designed to detect hydrogen gas at low levels and dissipate the gas to prevent accumulation.
The Battery Room Ventilation System (BRVS) incorporates the Ventilation Stands, Hydrogen Gas Detector (HGD), Hydrogen Exhaust Fan (HEF), and exhaust duct work into one complete system.
The HGD monitors hydrogen gas levels and provides warning of increasing levels before they become dangerous. The HGD controls the HEF; therefore, the powered exhaust fans will run when the concentration of hydrogen gas has reached 1 percent or greater. This feature will help a facility save money by both reducing the run time of the fans and by preventing the unnecessary escape of climate-controlled air.
The Ventilation Stands and connected exhaust duct network are designed to capture hydrogen gas without forced ventilation. As gas exits the batteries, it flows through a network of ducts to safely exit the building with the aid of the HEF.
Features & Benefits
- Increases battery room safety by monitoring hydrogen levels
- Improves battery room air quality by exhausting gases produced during battery charge
- Exhaust damper on each stand ensures even airflow throughout the entire system
- Spiral steel exhaust pipe for added durability
- Pipes are mounted to the stands, eliminating both the need to attach to rafters and issues caused by high ceilings
- Custom designs available to fit all your battery changing requirements
- A complete BRVS aids in compliance with the following standards: NEC 480.9 Ventilation of Battery Rooms, NEC 501.125. (B), 501.105 (1-3), NFPA 2 Hydrogen Technology Code
- Proudly designed and manufactured in the USA
View the Hydrogen Gas Ventilation Calculator for a free, online estimate of the possible level of hydrogen in a facility, and determine the necessary precautions that should be taken. Call 1.800.BHS.9500 to learn more or to find a local dealer.